Introduction to Software Testing
Software testing is an essential component of the development process, yet many people overlook its significance. Imagine pouring countless hours into coding a program, only to discover that it’s riddled with bugs when it hits the market. That’s where software testing swoops in as your safety net, ensuring quality and reliability before your product reaches users.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, understanding software testing basics can set you apart from the crowd. Whether you’re a developer looking to enhance your skills or a project manager wanting to streamline processes, grasping these concepts will empower you. Let’s dive deeper into this critical practice and uncover why every line of code deserves meticulous scrutiny!
Types of Software Testing
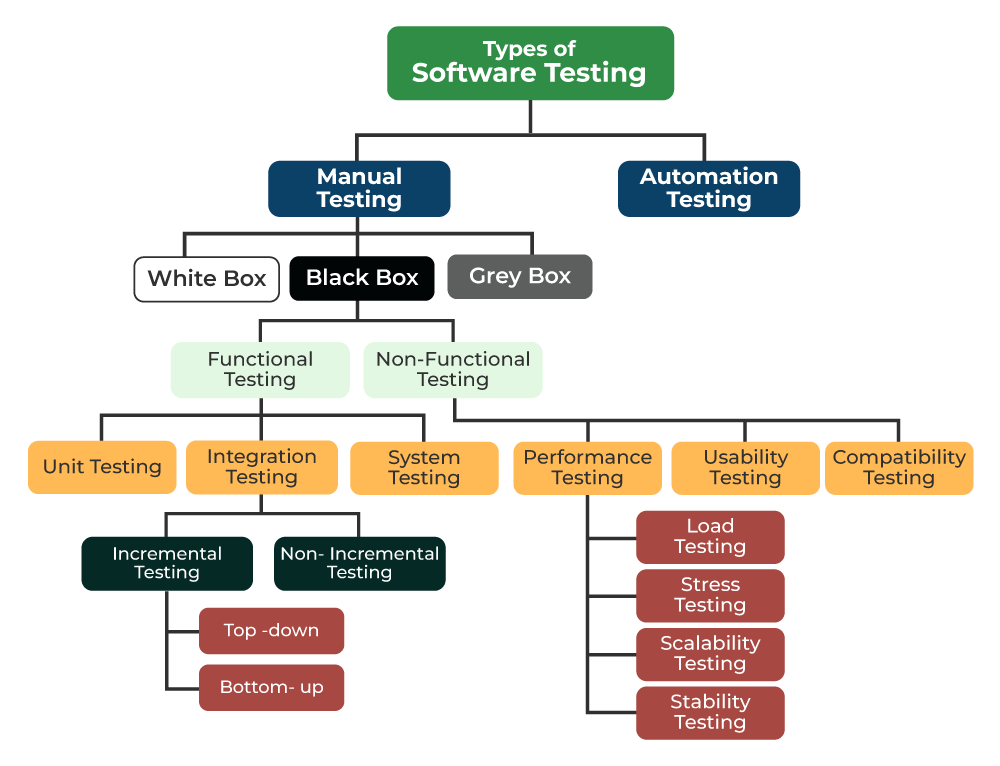
Software testing comes in various forms, each designed to address specific needs. Functional testing evaluates the software against functional requirements. It ensures that every feature works as intended.
Non-functional testing focuses on aspects like performance and usability. This type examines how the application behaves under load or its user-friendliness.
Manual testing relies on human testers to execute test cases without automated tools. It’s essential for exploratory scenarios where intuition matters.
Automated testing uses scripts and software tools to perform tests quickly and repeatedly. It’s particularly useful for regression tests, saving time in long-term projects.
Unit testing looks at individual components of the code base, ensuring they function correctly before integrating them into larger systems. Integration testing follows, checking how well those components work together.
Each type plays a crucial role in maintaining quality throughout the software development lifecycle. Understanding these types helps teams choose the right approach based on project requirements.
Importance of Software Testing
Software testing is crucial in today’s digital landscape. It ensures that applications perform seamlessly and meet user expectations. Without rigorous testing, software can fail, causing significant financial losses and damaging a company’s reputation.
Identifying bugs early saves time and resources. The cost of fixing issues during the development phase is far less than addressing them post-launch. Early detection also enhances customer satisfaction by delivering reliable products.
Moreover, software testing fosters innovation. By ensuring stability, developers are encouraged to explore new features without the fear of breaking existing functionalities.
In regulated industries like healthcare or finance, robust testing becomes mandatory to comply with legal standards and protect sensitive data. This practice not only safeguards users but also builds trust between businesses and their clients.
Effective software testing forms the backbone of any successful application lifecycle management strategy.
The Process of Software Testing
The process of software testing involves a systematic approach to ensure that the application functions as intended. It begins with planning, where testers define objectives and establish criteria for success. A well-crafted test plan is crucial at this stage.
Next comes test design. Test cases are written based on the requirements gathered during the planning phase. Each case outlines specific conditions under which tests will be executed, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
Execution follows, where testers run these cases in controlled environments. This step identifies defects or issues that need addressing before launch.
Once issues are found, they undergo prioritization and management. Developers fix these bugs while testers validate solutions through re-testing.
Results are documented thoroughly to provide insights into quality and performance metrics. This continuous loop of feedback helps refine future testing efforts and enhances overall software quality over time.
Common Techniques and Tools Used in Software Testing
Software testing employs various techniques and tools to ensure quality. Among the most common is manual testing, where testers execute test cases without automation. This method is ideal for exploratory testing and understanding user experience.
Automated testing has gained traction due to its efficiency. Tools like Selenium and JUnit allow testers to run repetitive tasks quickly and accurately. These tools save time while enhancing precision in large projects.
Performance testing evaluates how a system behaves under load. Tools such as Apache JMeter help identify bottlenecks before they become issues in production environments.
Moreover, security testing tools like OWASP ZAP assess vulnerabilities within applications. They play a vital role in safeguarding sensitive data from potential threats.
Continuous integration (CI) practices utilize platforms like Jenkins or Travis CI to automate tests during the development cycle, ensuring immediate feedback on code changes without disrupting workflow.
Challenges and Limitations in Software Testing
Software testing is essential, yet it faces several challenges. One major hurdle is time constraints. Teams often rush to meet deadlines, leading to inadequate testing.
Another significant limitation involves the complexity of modern software applications. With intricate systems and integrations, identifying all possible issues becomes a daunting task.
Additionally, resource availability can be an obstacle. Skilled testers are in high demand, and finding the right talent may prove difficult for many organizations.
Testing environments also introduce variability. Differences between production and testing settings can lead to undetected bugs when software goes live.
Keeping up with rapid technological advancements poses another challenge. New tools and methodologies emerge frequently, requiring ongoing adaptation from testing teams to stay effective in their roles.
Best Practices for Successful Software Testing
Establish clear requirements before starting any testing process. Understanding what the software should achieve helps identify critical areas that need attention.
Incorporate automated testing where possible. Automation speeds up repetitive tasks and allows for quicker releases, making it easier to manage large codebases.
Foster collaboration between testers, developers, and stakeholders. Open communication enhances understanding of issues and ensures everyone is aligned with project goals.
Regularly update test cases as the software evolves. Keeping your tests relevant prevents outdated methods from hindering progress or missing significant bugs.
Prioritize user experience by incorporating usability testing into your strategy. A product’s success hinges on its ability to meet user needs effectively.
Maintain detailed documentation throughout the testing lifecycle. This practice aids in tracking changes over time and serves as a valuable resource for future projects.
Conclusion
Software testing is a critical component of the software development lifecycle. Understanding its basics can significantly enhance the quality and performance of applications. By exploring different types, recognizing their importance, and following established processes, teams can ensure that products meet user expectations.
Navigating challenges in software testing requires awareness and adaptation. Utilizing common techniques and tools helps streamline efforts while maintaining thoroughness. Adopting best practices fosters an environment where testing not only identifies bugs but also enhances overall product reliability.
As technology evolves, so do methods for effective software testing. Staying informed about new trends ensures that your approach remains relevant and efficient. Prioritizing robust software testing ultimately leads to superior products that satisfy users and drive business success.