Introduction to Nukleotidy
Have you ever heard of nukleotidy? If not, you’re in for a fascinating journey into the world of these essential molecules. Nukleotidy play a crucial role in our bodies, influencing everything from cellular functions to overall health. As science continues to uncover their importance, more people are curious about how they can incorporate them into their diets and reap potential benefits.
In this blog post, we will dive deep into what nukleotidy are, why they’re vital for your health, and how you can easily add them to your daily routine. Let’s unravel the mysteries behind these tiny yet powerful components that hold the key to better health!
What are Nukleotidy?
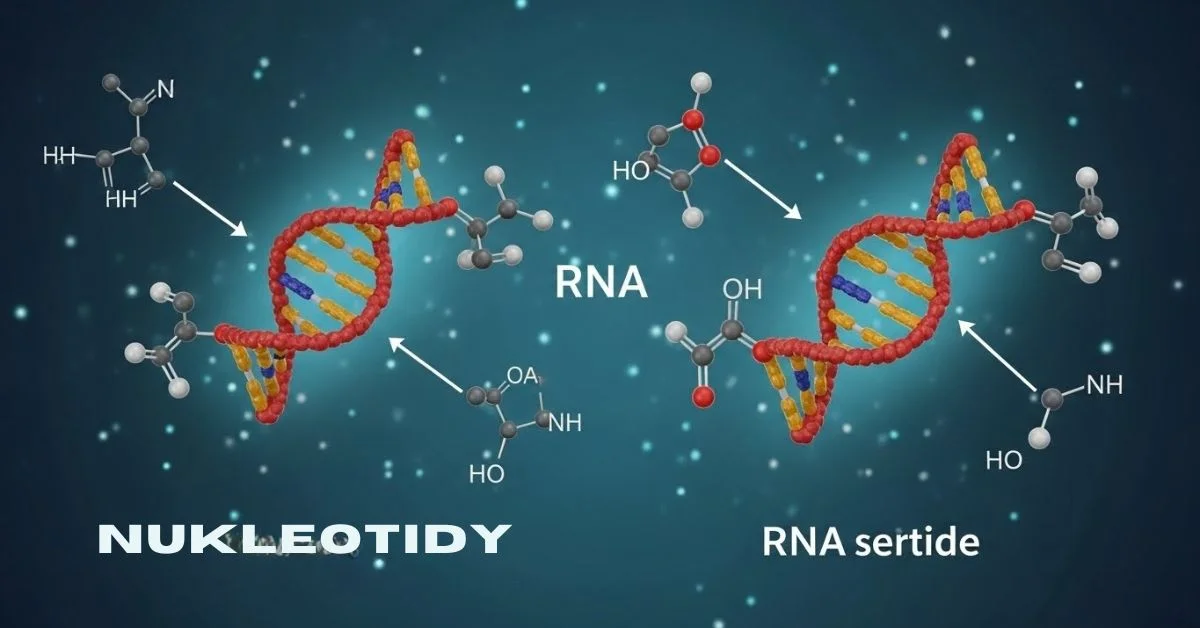
Nukleotidy, or nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They play a crucial role in storing and transmitting genetic information within cells.
Each nucleotide consists of three components: a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The sequence of these bases encodes biological instructions.
These tiny molecules are not just structural elements but also serve as energy carriers. ATP (adenosine triphosphate), for instance, is vital for cellular energy transfer.
Nukleotidy facilitate numerous biochemical processes including protein synthesis and cell signaling. Their diverse functions make them essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
The Importance of Nukleotidy in the Human Body
Nukleotidy play a crucial role in cellular function. They are the building blocks of DNA and RNA, vital for genetic material replication and protein synthesis. Without them, our cells would struggle to divide properly or produce essential proteins.
These compounds also participate in energy transfer within cells. ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a type of nukleotid, is known as the energy currency of the cell. It fuels various biochemical reactions that keep our bodies functioning efficiently.
Moreover, nukleotidy contribute to metabolic processes and aid in cellular signaling pathways. This interaction helps regulate numerous bodily functions including immune responses and tissue repair.
Their presence is fundamental not just for growth but also for overall health maintenance. Ensuring adequate levels can support optimal physiological activities throughout life’s stages.
Different Types of Nukleotidy and their Functions
Nukleotidy, or nucleotides, play various roles in our bodies. They are the building blocks of DNA and RNA, essential for genetic information storage and transfer.
Adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T) are key players in DNA. Each contributes to the formation of genes that dictate our traits.
In contrast, uracil replaces thymine in RNA. This subtle change is vital for protein synthesis.
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, serves as an energy currency within cells. It fuels countless biochemical processes critical for life.
NADH and FADH2 support cellular respiration by transporting electrons during energy production.
Each type of nukleotidy has a specific function that underpins biological processes. Their intricate interactions highlight their importance in maintaining health and supporting metabolic functions.
How to Incorporate Nukleotidy into Your Diet
Incorporating nukleotidy into your diet can be both simple and delicious. Start by focusing on whole foods that are naturally rich in these important compounds. Foods like fish, chicken, and beef are excellent sources.
Legumes such as beans and lentils also provide a healthy dose of nucleotides. Whole grains like quinoa or oats add variety while contributing to your intake.
Don’t overlook the benefits of dairy products too. Yogurt, milk, and cheese not only enrich your diet but also enhance nucleotide levels.
For those who prefer plant-based options, consider introducing nuts and seeds into your meals. They offer essential nutrients along with beneficial nucleotides.
If you’re looking for convenience, there are dietary supplements available specifically designed to boost nucleotide levels. Be sure to choose reputable brands that prioritize quality ingredients for maximum benefit.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Nukleotidy Supplementation
Nukleotidy supplementation has gained attention for its potential health benefits. These compounds play a crucial role in cellular processes, such as energy production and DNA repair. Many people turn to supplements to enhance their immune function and support gut health.
Some studies suggest that increasing nukleotidy intake may improve athletic performance by aiding muscle recovery and reducing fatigue. This makes them appealing for athletes or active individuals looking for an edge.
However, there are risks involved with taking these supplements without proper guidance. Excessive consumption could lead to imbalances within the body, potentially resulting in digestive issues or other side effects.
Individuals with specific medical conditions should consult healthcare professionals before starting any supplement regimen. Understanding personal health needs is essential when considering nukleotidy supplementation as part of your diet.
Conclusion: Is Nukleotidy Right for You?
Nukleotidy have become a topic of interest for many health enthusiasts. Their role in cellular function and genetic material is crucial, making them vital to our well-being. As you explore the potential benefits of incorporating nukleotidy into your diet or considering supplementation, it’s essential to weigh both their advantages and any possible risks.
If you’re looking to boost your energy levels, support recovery after workouts, or enhance overall health, adding foods rich in nukleotidy might be beneficial. However, before starting any new supplement regimen, consulting with a healthcare professional is wise.
Determining if nukleotidy are suitable for you depends on individual health needs and lifestyle choices. Whether through dietary sources like meat and fish or via supplements, understanding how these compounds fit into your routine can help guide your decision-making process regarding their inclusion in your daily life.